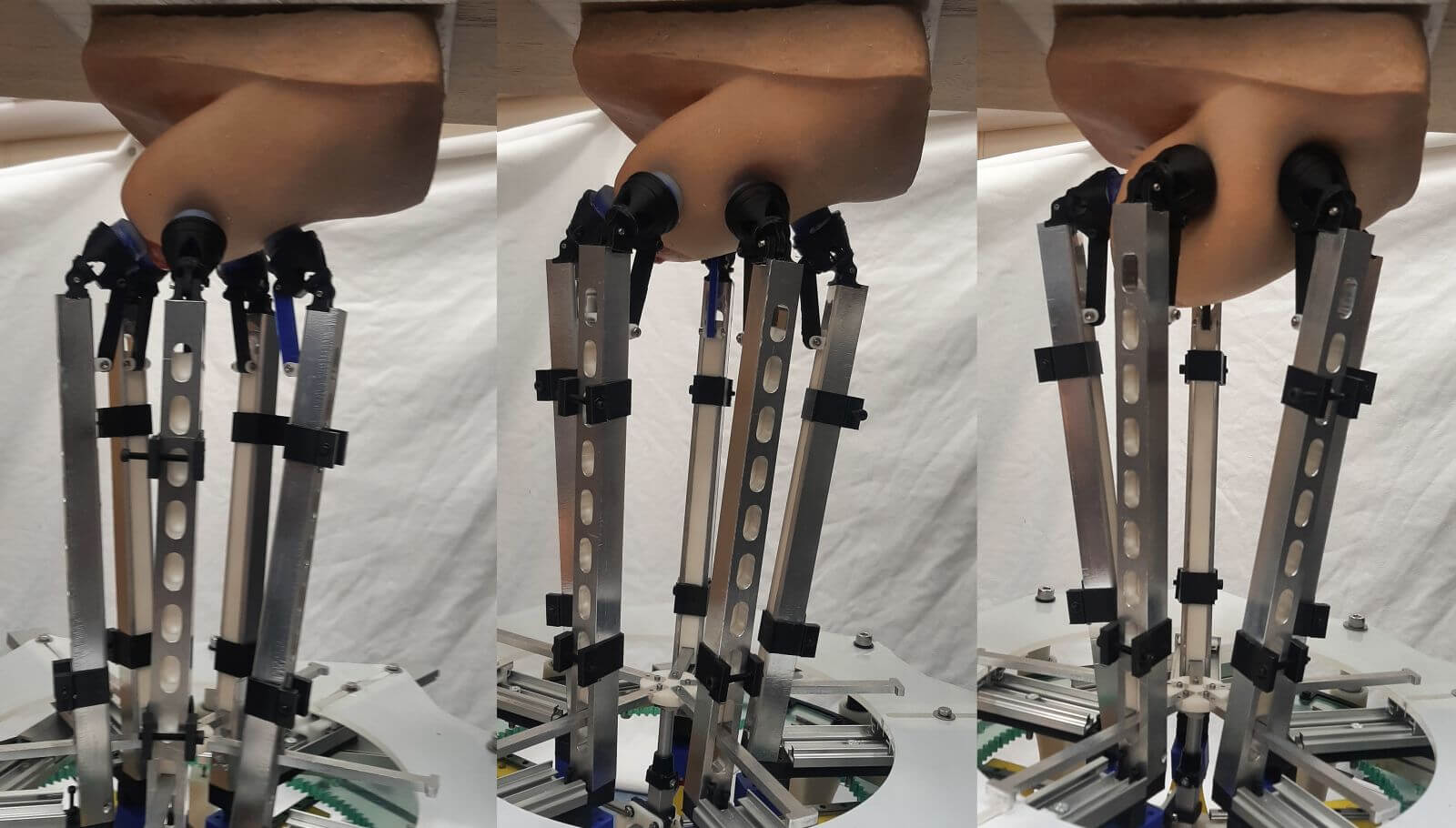
The University of Bristol has introduced a groundbreaking robot, aptly named the “manipulator,” designed by the Bristol Robotics Laboratory team to facilitate the early detection of breast cancer.
This innovative device was meticulously crafted using a 3D printer and has undergone rigorous testing through simulated experiments using a silicone breast model.
One of the robot’s primary applications is the early diagnosis of breast cancer, and it exhibits promising accuracy in detecting lumps during examinations.
Notably, this development could potentially revolutionize clinical breast examinations, making them more accessible and convenient. It opens the door to conducting these examinations in local pharmacies and similar settings.
George Jenkinson, the lead author of the project, expressed their aspirations for this innovative creation:
“We hope that in the future this could be a real help in diagnosing cancers early. There have been a few attempts in the past to use technology to improve these examinations, but having a robot or electronic device that can physically feel breast tissue could be revolutionary.”
“We hope that the research can help identify large-scale trends that could help diagnose breast cancer early,” added Mr. Jenkinson. “The ultimate goal is that the device and sensors will have the capability to detect lumps more accurately and deeper than is possible only from applying human touch.”
Reports reveal that Nigeria has some of the highest breast cancer (BC) mortality rates globally, with the country bearing the highest BC mortality rate in Africa.
The incidence of BC in Nigeria is on the rise, with the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) documenting 28,380 new BC cases in the country in 2020. This accounted for 22.7% of all newly reported cancer cases and represented the largest share among various cancer types in Nigeria.
Given the lack of comprehensive data on BC treatment and outcomes in Nigeria, it becomes imperative to identify research gaps, challenges, and potential areas for future interventions.
Late diagnosis has been extensively studied as a significant contributing factor to the high morbidity and mortality rates associated with BC. Thus, this innovative robot holds the potential to play a crucial role in aiding early detection, which is vital in combating this devastating disease.